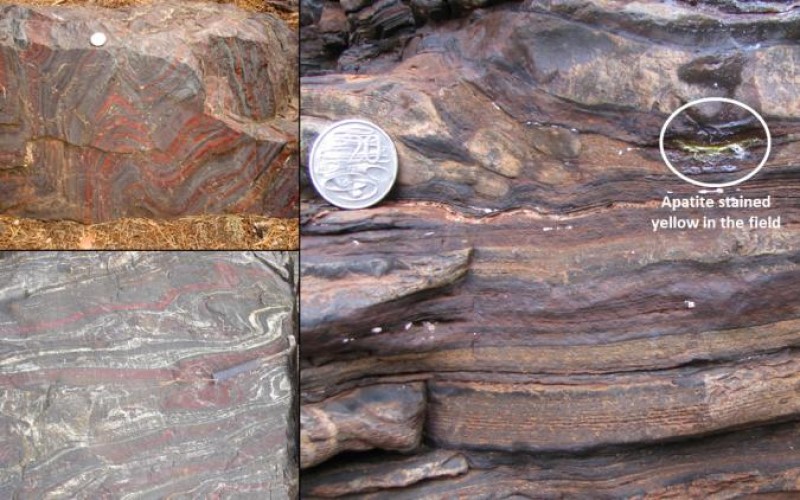
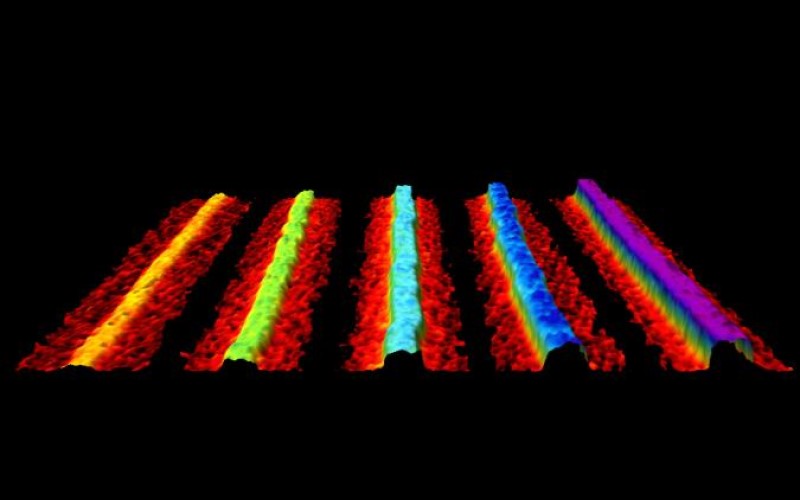


Tracking records of the oldest life forms on Earth
Ancient organic matter of biological origin has been tracked in multiple samples of rock spanning over 2,000 million years of Earth’s history, according to LCN researchers. The discovery provides a new characteristic ‘bio-signature’ to track the remains of ancient...
Building the future of mobile healthcare
The combination of mobile devices with diagnostic tools offers new possibilities to test, track and treat infectious diseases as well as improve health systems, according to a new review published today in Nature. The review, led by i-sense researchers from the London...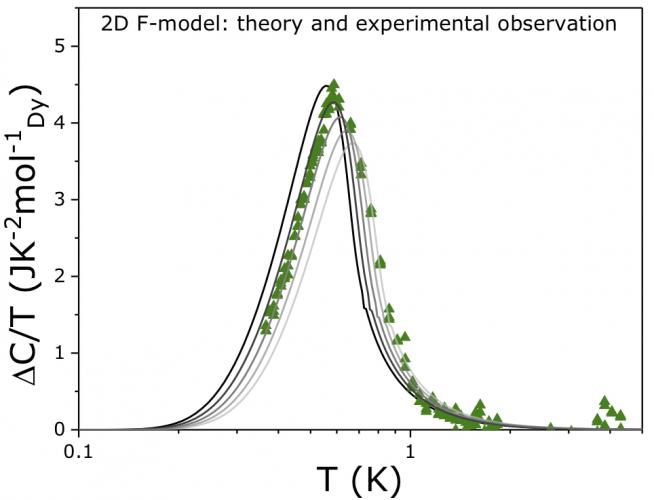
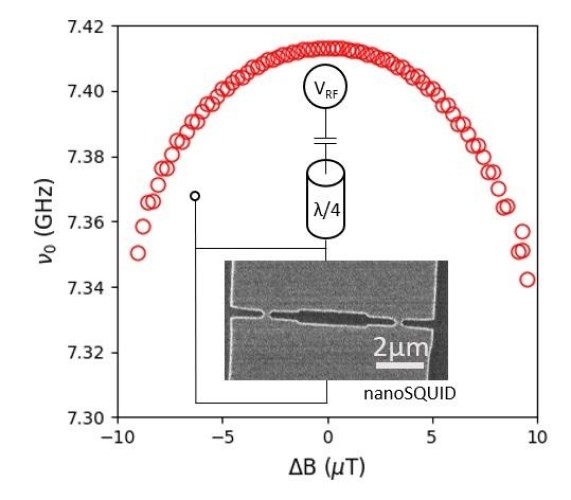
LCN researchers observe many-body physics in an atomic layer of spin ice
A half-century old prediction about how a sheet of atoms will behave has been experimentally verified by researchers at the LCN. Any familiar lump of matter – whether a drop of water or a grain of salt – contains a lot of atoms, typically up to a trillion trillion....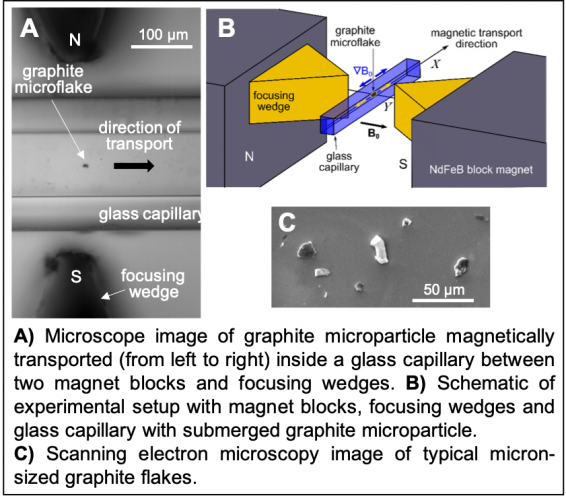
Moving graphite particles in liquid using magnetism
A way of transporting tiny particles of graphite in liquid using magnetic fields has been developed by UCL scientists. It opens up possibilities for new ways of precisely transporting specific components in fluids, including in biocompatible fluids such as in the...