Healthcare
The development of new drug delivery systems using nanoparticles to target specific cells in the body, along with the creation of medical devices and diagnostic tools based on nanotechnology, is leading to innovative and effective solutions for disease prevention, diagnosis, and treatment.
Diagnostic AND Monitoring
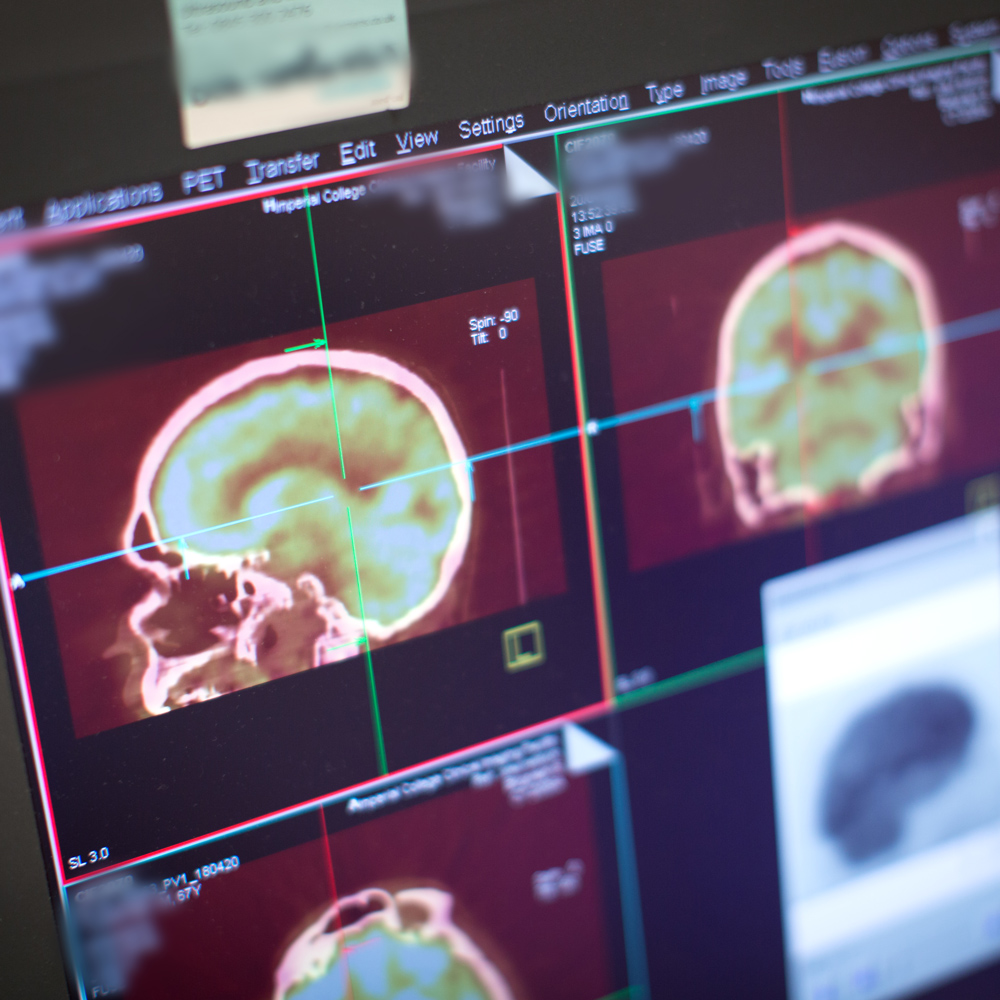
Nanotechnologies can support early detection, continuous monitoring, and high-resolution diagnostics, paving the way for proactive, personalised medicine with improved outcomes. Nanoparticles can be engineered to target specific biomarkers, enabling real-time imaging and precise diagnostics at the molecular level.


Healthy environment
Through innovations like targeted drug delivery, nanoscale diagnostics, and biodegradable materials, nanotechnology minimises the ecological footprint of medical treatments.
Mechanisms of life
Mechanisms of life refer to the molecular and cellular processes that sustain biological functions, such as DNA replication, protein synthesis, and cellular signaling. Nanotechnology enables precise manipulation and observation of these mechanisms at the nanoscale, allowing for early disease detection, targeted drug delivery, and regenerative medicine. By interfacing directly with biological systems, nanodevices can mimic, repair, or enhance natural processes, revolutionising personalised medicine and diagnostics.

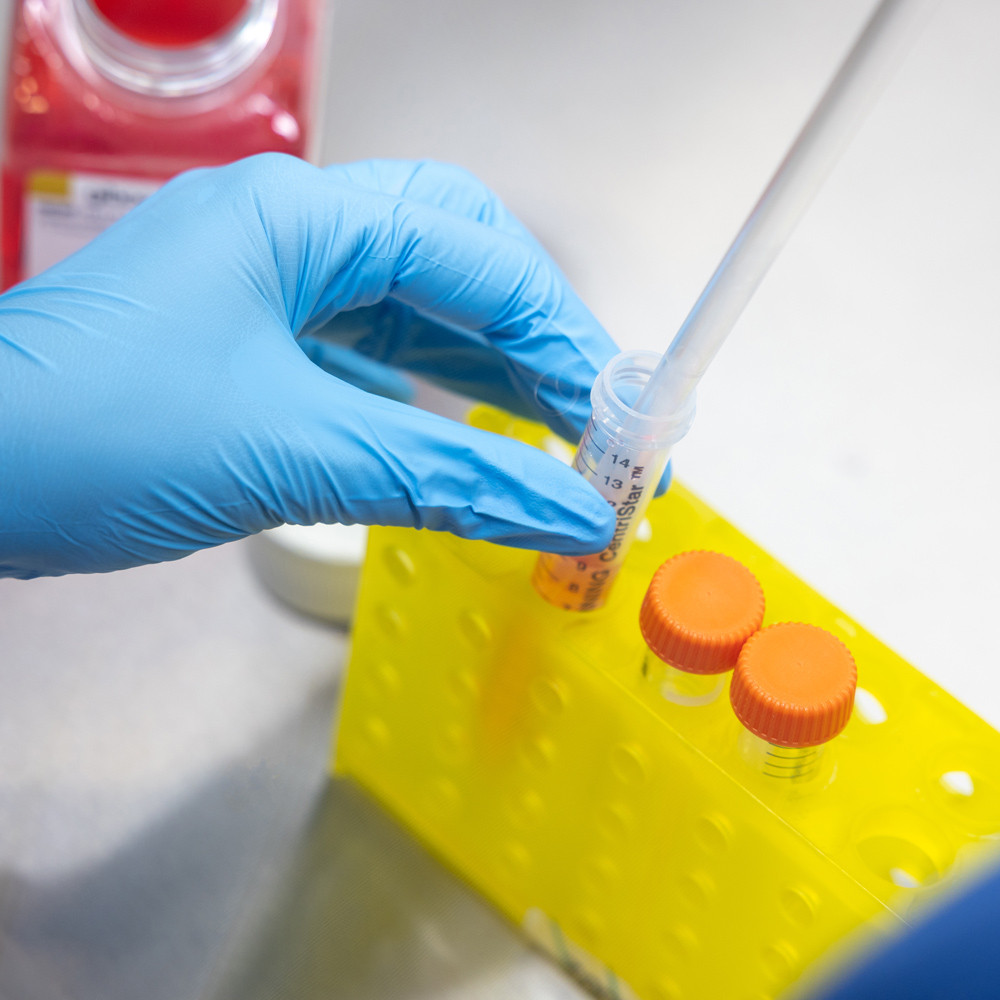
Therapeutic agents and delivery
Therapeutic agents and delivery refers to the development and use of nanotechnology to enhance the effectiveness, precision, and safety of treatments. Nanoparticles can be engineered to carry drugs directly to diseased cells minimising side effects and improving drug bioavailability. This targeted delivery allows for lower doses, reduced toxicity, and better patient outcomes. Additionally, nanocarriers can be designed for controlled or sustained release, further optimising therapeutic efficacy.
Tissue engineering and implants
Tissue engineering and implants involve the development of biomimetic materials at the nanoscale to repair, replace, or regenerate damaged tissues and organs. Nanotechnology enhances these solutions by improving cell adhesion, proliferation, and differentiation through nano-structured scaffolds and surfaces. Additionally, nanomaterials can be used to deliver bioactive agents precisely, promote integration with the host tissue, and reduce the risk of rejection or infection. This interdisciplinary approach holds promise for creating more effective, personalised, and long-lasting medical implants and regenerative therapies.
Our people
The LCN is home to 240 principal investigators, 300 post doctoral researchers, and 500 PhD students
Healthcare news

Quantum-powered rapid tests using nanodiamonds could detect covid much earlier
In research published in Nature Communications earlier this month, some of our scientists have demonstrated that their spin-enhanced ... Find out more

Startling images show how antibiotic pierces bacteria’s armour
A team led by UCL and Imperial College London researchers has shown for the first time how life-saving antibiotics called polymyxins ... Find out more
